At its core, vulcanization is a chemical process that transforms soft, sticky natural rubber into a durable, elastic, and highly useful material. By heating raw rubber with sulfur and other curing agents, a fundamental change occurs at the molecular level, creating a product that is strong, flexible, and resistant to temperature changes.
Natural rubber in its raw state is too weak and unstable for most practical applications. Vulcanization solves this by using sulfur to create chemical "bridges" between rubber molecules, locking them into a robust, elastic structure.

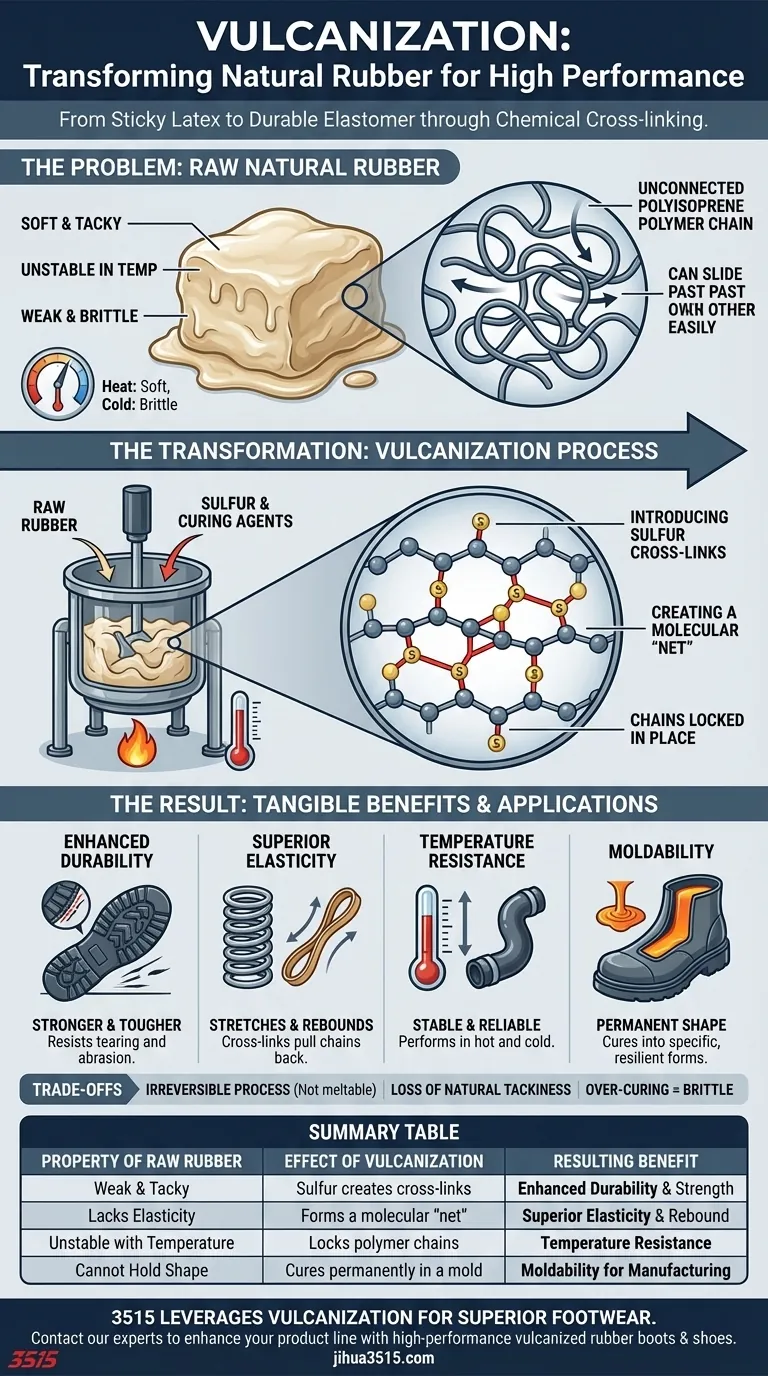
The Problem with Raw Natural Rubber
To understand why vulcanization is so crucial, we must first look at the limitations of rubber in its natural state.
A Sticky and Unstable Material
Raw natural rubber, or latex, is a tacky, weak substance. It becomes soft and sticky in the heat and brittle in the cold, making it unreliable for any application requiring consistency.
The Molecular View
At a microscopic level, natural rubber is made of long, tangled polymer chains (polyisoprene). These chains are not chemically connected and can easily slide past one another, which is why the material deforms so easily and lacks strength.
How Vulcanization Transforms the Material
The process, famously perfected by Charles Goodyear, introduces a chemical change that permanently alters these properties for the better.
Introducing Sulfur Cross-links
The key ingredient is sulfur. When heated with rubber, sulfur atoms insert themselves between the long polymer chains, creating strong chemical bonds known as cross-links.
Creating a Molecular "Net"
You can think of these sulfur cross-links as the rungs of a ladder connecting two long side rails (the polymer chains). This creates a single, unified molecular network, or "net." The chains can no longer slide apart freely.
The Resulting Properties
This new molecular structure is what gives vulcanized rubber its celebrated characteristics. The material is now set into a stable, permanent form.
The Tangible Benefits of the Transformation
The shift from a loose collection of polymer chains to a cross-linked network results in dramatic improvements in performance.
Enhanced Durability
The molecular net makes the rubber significantly stronger and tougher. It can resist tearing and abrasion, which is why it's ideal for products like vehicle tires and shoe soles.
Superior Elasticity
While the cross-links prevent the chains from sliding apart permanently, they still allow them to stretch and uncoil. When the force is removed, the cross-links pull the chains back to their original position, giving rubber its signature elasticity.
Temperature Resistance
Vulcanization makes rubber far more stable across a wide range of temperatures. It no longer becomes gooey when hot or fragile when cold, making it a reliable material for engine hoses, seals, and outdoor equipment.
Moldability for Manufacturing
The process allows the soft, pliable raw rubber to be shaped in a mold—like for a rubber boot—and then vulcanized. The heating process cures and permanently sets the rubber into that specific, durable shape.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While revolutionary, the process is not without its compromises. True understanding requires acknowledging its limitations.
It's an Irreversible Process
Once rubber is vulcanized, it cannot be melted down and easily reshaped like a thermoplastic. The chemical cross-links are permanent, which makes recycling more complex.
Loss of Natural Tackiness
The very stickiness that makes raw rubber problematic in a final product is actually useful during manufacturing for building up layers. Vulcanization permanently removes this tack.
Brittleness if Over-cured
The process must be carefully controlled. Adding too much sulfur or applying heat for too long can create too many cross-links, making the rubber hard and brittle rather than strong and elastic.
How to Apply This Understanding
Recognizing the "why" behind vulcanization helps you better understand the properties of countless objects you interact with daily.
- If your primary focus is on product durability: See vulcanization as the reason the soles of your shoes can bend thousands of times without breaking and why car tires can withstand immense friction.
- If your primary focus is on material science: Understand this process as the fundamental method for converting a natural polymer into a high-performance thermoset elastomer.
- If your primary focus is on design and manufacturing: Recognize that vulcanization is what allows a flexible raw material to be permanently molded into a specific, resilient form, from a simple O-ring to a complex boot.
Ultimately, vulcanization is the chemical key that unlocked the vast potential of rubber, transforming a raw natural substance into an indispensable material of the modern world.
Summary Table:
| Property of Raw Rubber | Effect of Vulcanization | Resulting Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Weak & Tacky | Sulfur creates cross-links | Enhanced Durability & Strength |
| Lacks Elasticity | Forms a molecular "net" | Superior Elasticity & Rebound |
| Unstable with Temperature | Locks polymer chains | Temperature Resistance |
| Cannot Hold Shape | Cures permanently in a mold | Moldability for Manufacturing |
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 leverages vulcanization to produce superior, durable footwear. Our expertise in this chemical process ensures every pair of boots or shoes for our distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients offers unmatched strength, elasticity, and longevity. Ready to enhance your product line with high-performance vulcanized rubber footwear? Contact our experts today to discuss your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Durable Camo Canvas Shoes with High-Traction Rubber Soles
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Wholesale Comfortable Business Casual Shoes Custom Manufacturing
- Durable Spiked Camouflage Boots Wholesale & Factory Production
- Wholesale Comfort Leather Business Shoes with Dial Lacing System
People Also Ask
- What is ASTM International and what does it do? A Guide to Global Standards
- What organization sets national standards for workplace safety in the U.S.? OSHA's Role Explained
- What types of clothing are not considered business casual? Avoid These Common Style Mistakes
- Do people never lack motivation to work out? The Truth About Fitness Consistency
- What is the purpose of ASTM International? A Guide to Global Quality Standards



















