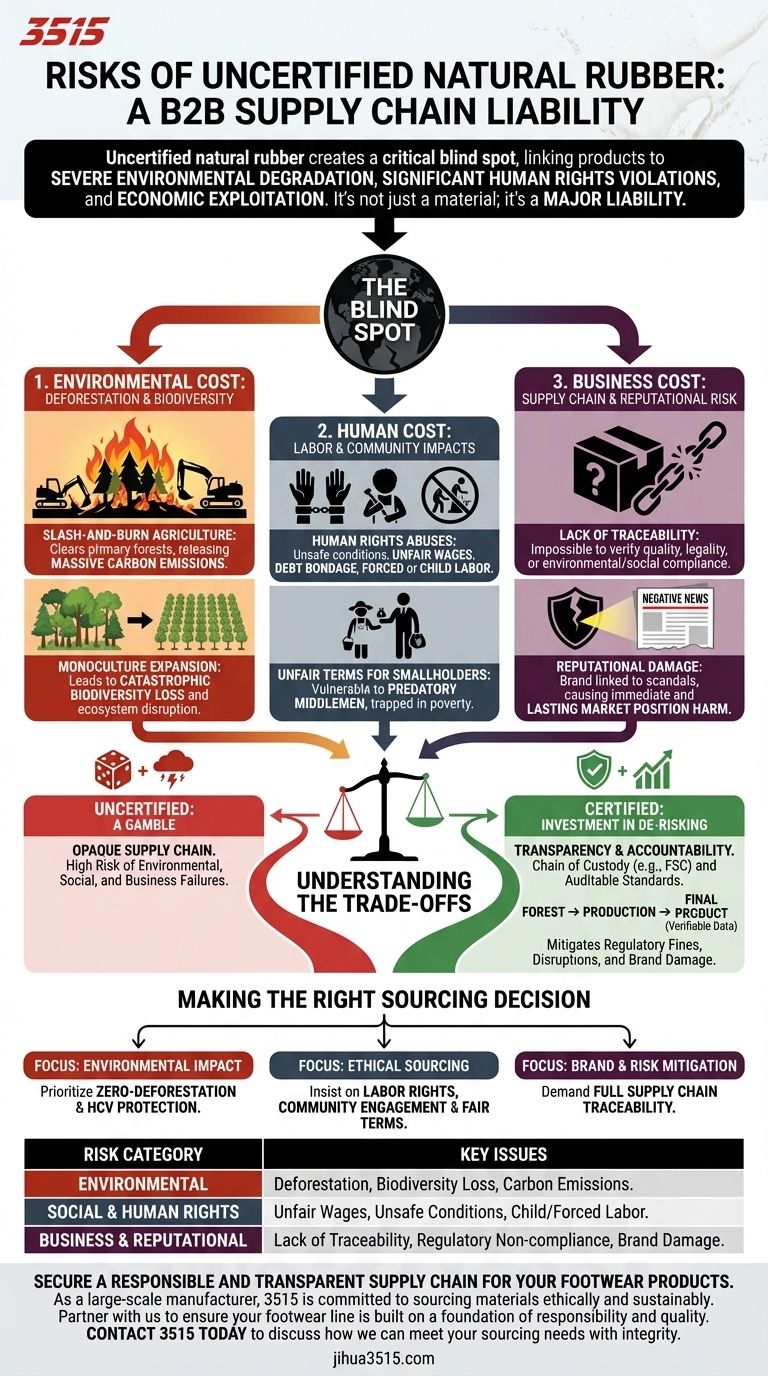
In short, the primary risks of using uncertified natural rubber are severe environmental degradation, significant human rights violations, and economic exploitation. Sourcing rubber without certification creates a critical blind spot in your supply chain, potentially linking your products directly to deforestation and unethical labor practices.
Uncertified natural rubber is not merely a material; it's a liability. The lack of certification obscures a supply chain fraught with unacceptable environmental, social, and business risks that can damage ecosystems, communities, and your brand's reputation.

The Environmental Cost: Deforestation and Biodiversity
The demand for rubber is a powerful driver of land-use change, particularly in Southeast Asia. An uncertified supply chain offers no protection against its destructive potential.
How Rubber Drives Deforestation
Uncertified rubber plantations often expand by clearing irreplaceable primary and secondary forests. This process, known as slash-and-burn agriculture, releases massive amounts of carbon into the atmosphere and destroys vital ecosystems.
Without the standards enforced by certification, there is no mechanism to ensure that rubber production is confined to previously degraded land or existing agricultural zones.
The Impact on Biodiversity
These forests are critical habitats for thousands of species, many of which are endangered. The conversion of diverse forests into vast, single-crop monoculture plantations leads to catastrophic biodiversity loss, disrupting local ecosystems and food webs.
The Human Cost: Labor and Community Impacts
The lack of oversight in uncertified rubber supply chains creates conditions ripe for exploitation, affecting both hired laborers and the small-scale farmers who produce the majority of the world's rubber.
The Risk of Human Rights Abuses
Uncertified operations have been linked to severe labor rights issues. These can include unsafe working conditions, unfair wages, debt bondage, and, in the worst cases, forced or child labor.
Certification bodies mandate standards for worker safety, fair compensation, and freedom of association, providing a crucial layer of protection that is absent in uncertified systems.
Unfair Terms for Smallholders
Smallholder farmers are the backbone of the rubber industry, but they often lack the market power to negotiate fair prices. In an opaque, uncertified market, they are vulnerable to predatory middlemen who capture most of the profit, trapping farmers in cycles of poverty.
The Business Cost: Supply Chain and Reputational Risk
For any modern business, sourcing uncertified materials is a significant strategic gamble. The risks extend far beyond the ethical and environmental, directly impacting operational stability and brand value.
Lack of Traceability
The most immediate business risk is a complete lack of supply chain traceability. If you don't know the precise origin of your rubber, you cannot verify its quality, legality, or compliance with any environmental or social standards. This creates profound operational and regulatory uncertainty.
Reputational Damage
Consumers, investors, and regulators are increasingly demanding transparency and sustainability. A report linking your brand to deforestation or human rights abuses—however indirectly—can cause immediate and lasting damage to your reputation and market position.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing certified rubber isn't about adding a "nice-to-have" feature; it's about fundamentally de-risking your supply chain and aligning your business with modern expectations.
What Certification Provides: Transparency
Certification programs, such as those from the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), establish a chain of custody. This creates a transparent path from the forest to the final product, replacing uncertainty with verifiable data.
What Certification Provides: Accountability
These programs set clear, auditable standards for environmental management, social responsibility, and economic fairness. They provide a framework for accountability that is simply absent in the uncertified market.
The Cost of Certification vs. The Price of Risk
While certified materials may carry a price premium, this should be viewed as an investment in risk mitigation. The potential cost of a supply chain disruption, a regulatory fine, or a brand-damaging scandal far outweighs the upfront cost of responsible sourcing.
Making the Right Sourcing Decision
Your sourcing strategy should be guided by a clear understanding of your organization's priorities, from risk management to corporate responsibility.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact: Prioritize certifications that guarantee zero-deforestation and the protection of High Conservation Value (HCV) areas.
- If your primary focus is ethical sourcing: Insist on certifications that have robust criteria for labor rights, community engagement, and fair economic terms for smallholders.
- If your primary focus is brand and risk mitigation: Demand full supply chain traceability, which is a core component of any credible certification scheme.
Choosing to source certified natural rubber is a decisive step toward building a more resilient, responsible, and reputable business.
Summary Table:
| Risk Category | Key Issues |
|---|---|
| Environmental | Deforestation, biodiversity loss, carbon emissions from slash-and-burn. |
| Social & Human Rights | Unfair wages, unsafe labor conditions, child/forced labor, exploitation of smallholders. |
| Business & Reputational | Lack of supply chain traceability, regulatory non-compliance, severe brand damage. |
Secure a responsible and transparent supply chain for your footwear products.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 is committed to sourcing materials ethically and sustainably. We understand that your brand's reputation depends on a transparent supply chain, free from the environmental and social risks of uncertified rubber.
Partner with us to ensure your footwear line is built on a foundation of responsibility and quality. We provide comprehensive solutions for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients.
Contact 3515 today to discuss how we can meet your sourcing needs with integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Factory-Direct Wholesale Canvas Boots with High-Traction Rubber Soles
- Factory Direct Wholesale Rain Boots Durable Waterproof & Fully Customizable
- Wholesale Durable & Breathable Training Shoes for Custom Brands
- Wholesale Comfortable Business Casual Shoes Custom Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- How do integrated FSR in sensing insoles prevent diabetic foot ulcers? Smart Monitoring for Diabetic Foot Health
- Why are industrial-grade split-belt treadmills essential for simulating slipping? Master Perturbation Research Precision
- What are the steps to clean leather cowboy boots? A Pro Guide to Long-Lasting Boots
- How can reckless behavior lead to workplace injuries? Prevent Costly Accidents & Boost Safety
- What is business casual attire in the workplace? Master the Dress Code for a Polished Look
- What are the functions of global logistics tracking and material flow software in textile and footwear production?
- How do high-efficiency air compression systems contribute to green footwear manufacturing? Boost Sustainability Today
- How does double stitching in Goodyear welted shoes improve durability? A 2-Stitch System for Decades of Wear



















