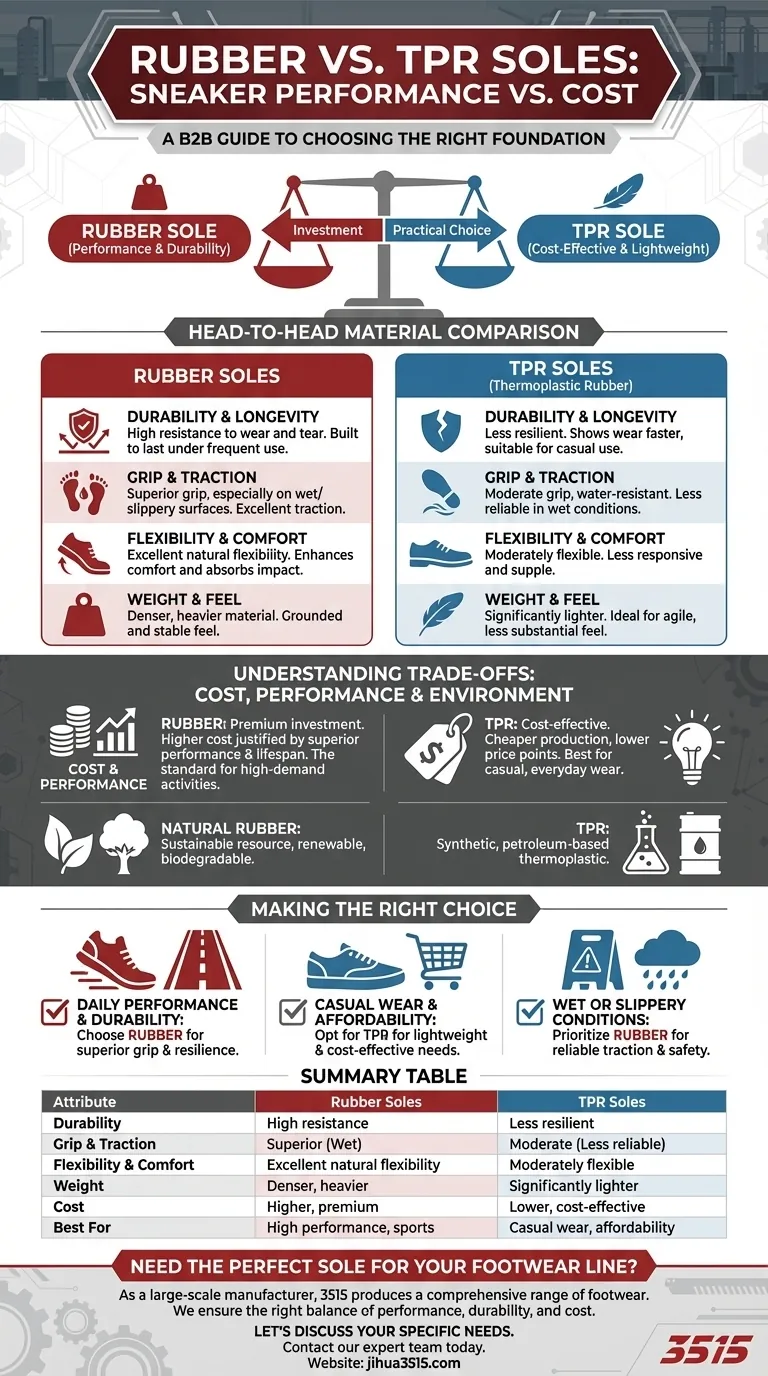
At a glance, the choice between rubber and TPR soles comes down to a trade-off between performance and cost. Rubber soles are the superior choice for durability, flexibility, and grip, making them ideal for premium, long-lasting footwear. In contrast, TPR (Thermoplastic Rubber) soles are a synthetic alternative prized for being lightweight and cost-effective, but they do not match the resilience or traction of true rubber.
The core difference is purpose-driven: Rubber is an investment in high performance and durability, while TPR is a practical choice for lightweight, affordable, casual footwear. Understanding this distinction is key to selecting the right sneaker for your needs.

A Head-to-Head Material Comparison
To make an informed decision, it's essential to understand how each material performs across key attributes that define a sneaker's foundation.
Durability and Longevity
Rubber is known for its high resistance to wear and tear. A quality rubber sole is built to last, handling frequent use and abrasive surfaces without degrading quickly.
TPR is less resilient. While durable enough for casual wear, it will typically show signs of wear much faster than a rubber sole, especially with frequent or intense use.
Grip and Traction
Rubber offers superior grip, especially on wet or slippery surfaces. Its natural properties provide excellent traction, which is a critical safety and performance feature.
TPR is water-resistant but does not provide the same level of grip as rubber. In extremely wet conditions, its performance can be noticeably less reliable.
Flexibility and Comfort
Rubber provides excellent natural flexibility, which enhances comfort by allowing your foot to move without restriction. Its cushioning properties also help absorb impact.
TPR is moderately flexible and allows for a decent range of movement. However, it doesn't quite match the supple, responsive feel of a high-quality rubber sole.
Weight and Feel
TPR has a distinct advantage in weight. It is a significantly lighter material, making it ideal for those who prefer footwear that feels less substantial and more agile for casual use.
Rubber is a denser, heavier material. This weight often contributes to a more grounded and stable feel but can be a drawback for those seeking the lightest possible sneaker.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Performance
Beyond the physical properties, the manufacturing and environmental implications create a clear divide between these two materials.
The Cost Factor
The primary driver for using TPR is its cost-effectiveness. It is cheaper to produce than rubber, which allows manufacturers to offer sneakers at a more accessible price point.
This makes rubber the material of choice for premium footwear. Its higher material and processing costs are justified by its superior performance and lifespan.
The Performance Ceiling
For any activity where grip and resilience are non-negotiable—such as court sports, hiking, or demanding daily wear—rubber is the undisputed standard. Its properties provide a higher ceiling for performance.
TPR is best suited for casual, everyday sneakers where the demands are low and the priority is on comfort, light weight, and affordability.
The Environmental Angle
Natural rubber is a sustainable resource. It is harvested from trees, is renewable, and is biodegradable, giving it a significant environmental advantage.
TPR, as a thermoplastic, is a synthetic, petroleum-based material. While it can be recycled, its production and end-of-life impact are different from those of its natural counterpart.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your ideal sole material depends entirely on how you plan to use your sneakers. Use these points as a definitive guide.
- If your primary focus is daily performance and long-term durability: Choose rubber soles for their superior grip, resilience, and comfort under stress.
- If your primary focus is casual wear and affordability: Opt for TPR soles to get a lightweight and cost-effective sneaker suitable for everyday, non-demanding use.
- If your primary focus is activities in wet or slippery conditions: Prioritize rubber soles, as their traction is significantly more reliable and a critical safety feature.
By understanding this fundamental trade-off between performance and practicality, you can confidently select footwear with a foundation perfectly suited to your needs.
Summary Table:
| Attribute | Rubber Soles | TPR Soles |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Less resilient, wears faster |
| Grip & Traction | Superior, especially on wet surfaces | Moderate, less reliable in wet conditions |
| Flexibility & Comfort | Excellent natural flexibility and cushioning | Moderately flexible, less responsive |
| Weight | Denser and heavier | Significantly lighter |
| Cost | Higher, premium option | Lower, cost-effective option |
| Best For | High performance, sports, long-term durability | Casual wear, affordability, lightweight needs |
Need the Perfect Sole for Your Footwear Line?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, ensuring you get the right balance of performance, durability, and cost for your target market.
Let's discuss your specific needs and find the ideal sole material for your next project.
Contact our expert team today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom OEM Training Shoes Wholesale Manufacturer Durable & Breathable
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Safety Shoes with Rotating Buckle Safety Sneakers
- Wholesale Leather Ankle Boots with Lug Soles for Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
People Also Ask
- What is the relationship between footwear design and the effectiveness of biomechanical alignment? Maximize Stability
- How can high-quality tactical or athletic footwear mitigate social participation restrictions? Enhance Your Mobility
- What is the benefit of using a multi-functional training station for CRT? Maximize Efficiency & Metabolic Health
- What key functions do professional Training Shoes perform? Maximize Stability and Power in High-Load Lifting
- What role do professional training shoes play during HIIT for adolescent athletes? Stability and Injury Prevention



















