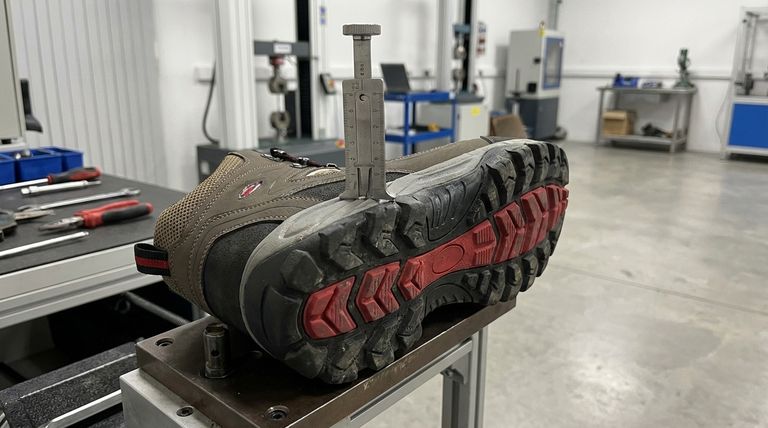
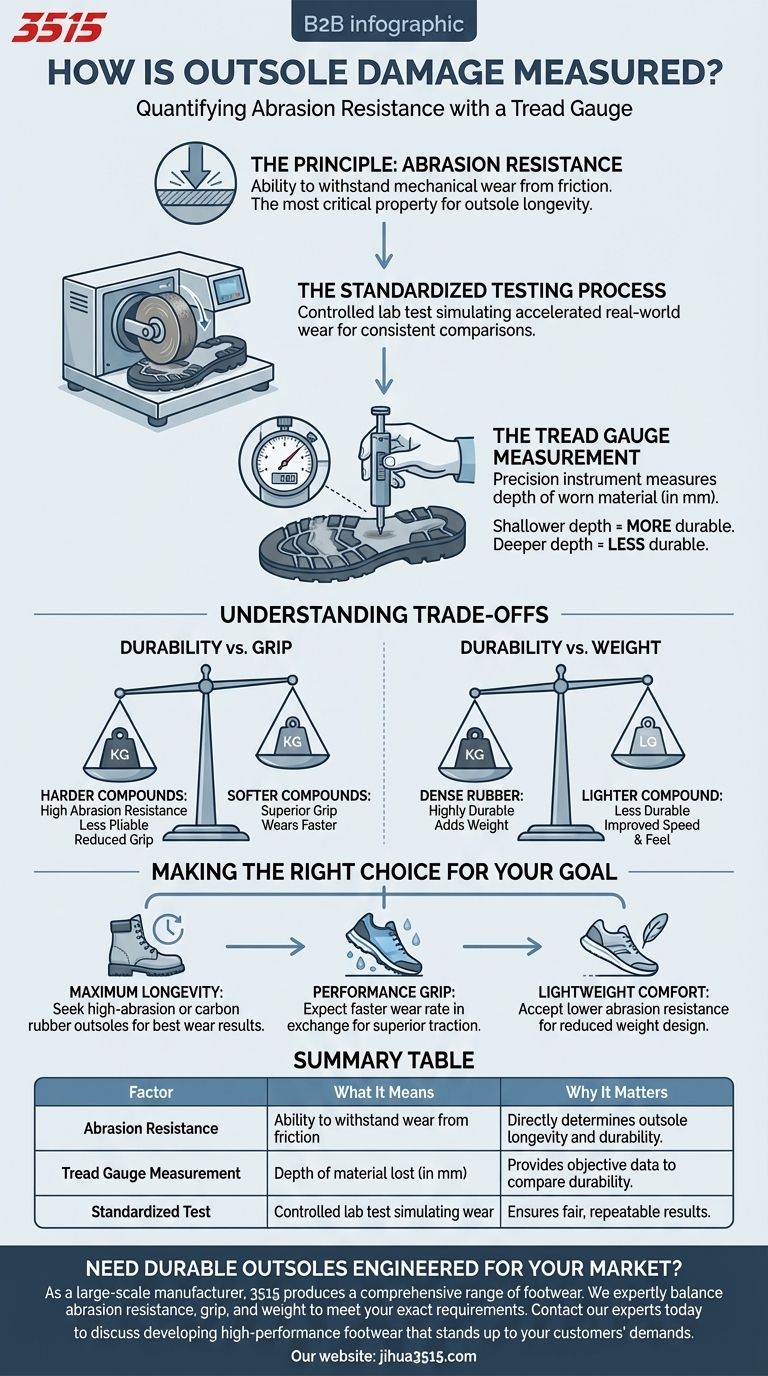
At its core, outsole damage is a measurement of abrasion resistance, which is quantified using a precision tool called a tread gauge. This instrument measures the depth of material worn away after a standardized test. A shallower measurement indicates less material was lost, signifying a more durable and abrasion-resistant outsole.
The critical insight is not just the tool used, but the principle it measures. True outsole durability is determined by its abrasion resistance—its ability to withstand friction without losing material—and a tread gauge provides the objective data to prove it.

The Principle Behind Measuring Outsole Wear
To understand the measurement, you must first understand the property being tested. The goal is to create a controlled, repeatable way to assess how an outsole material will hold up to real-world friction.
What is Abrasion Resistance?
Abrasion resistance is the fundamental ability of a material to withstand mechanical wear, such as scraping, rubbing, and erosion.
For a shoe outsole, this is the single most important property for longevity. It dictates how quickly the sole will wear down from constant contact with surfaces like pavement, trails, and flooring.
The Standardized Testing Process
A measurement from a tread gauge is only meaningful if it's taken after a standardized test. This ensures a fair comparison between different materials.
The process typically involves taking a sample of the outsole compound and subjecting it to a controlled abrasive force for a specific duration, often using a specialized machine with a rotating abrasive wheel or surface.
This controlled process simulates accelerated real-world wear in a laboratory setting.
How the Tread Gauge Works
After the abrasion test is complete, the tread gauge is used to measure the result.
It is a precision instrument that measures depth. An operator places the gauge over the worn area to determine exactly how much material, typically in millimeters, was eroded during the test.
A shallower dent or groove means the material successfully resisted the abrasion. A deeper measurement indicates the material wore away more easily.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A high score in abrasion resistance doesn't automatically make an outsole "better." It simply makes it more durable against friction. This property must be balanced with other critical performance factors.
Durability vs. Grip
There is often an inverse relationship between hardness and grip.
Extremely hard rubber compounds that excel in abrasion tests can be less pliable and offer reduced traction, especially on wet or smooth surfaces. Softer, "stickier" compounds provide superior grip but will wear down much faster.
Durability vs. Weight
Highly durable, dense rubber adds weight to a shoe.
In performance footwear, designers might use less rubber or a lighter compound to save weight, intentionally sacrificing some long-term durability for improved speed and a lighter feel. This is a deliberate engineering compromise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how outsole wear is measured helps you interpret a shoe's design and choose the right footwear for your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is maximum longevity: Seek out footwear that emphasizes its use of high-abrasion or carbon rubber, as these materials are engineered to produce the best results in wear testing.
- If your primary focus is performance grip: Recognize that a softer outsole that provides excellent traction is a feature, and its faster wear rate is an expected trade-off for that specific benefit.
- If your primary focus is lightweight comfort: Accept that minimal or softer outsoles are part of the design to reduce weight, which will inherently result in lower abrasion resistance.
By understanding this measurement, you can move beyond marketing and assess whether a shoe's outsole is truly engineered for your intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Factor | What It Means | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasion Resistance | The material's ability to withstand wear from friction. | Directly determines outsole longevity and durability. |
| Tread Gauge Measurement | The depth of material lost (in mm) after a standardized test. | Provides objective data to compare the durability of different outsoles. |
| Standardized Test | A controlled lab test simulating real-world wear. | Ensures fair, repeatable, and comparable results across materials. |
Need durable outsoles engineered for your specific market?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We expertly balance abrasion resistance, grip, and weight to meet your exact performance and longevity requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss developing high-performance footwear that stands up to your customers' demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Premium Safety Shoes with Rotating Buckle Safety Sneakers
- Premium Wholesale Wheat Nubuck Safety Boot with Rapid Lacing System
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- Why is proper cowboy boot sizing important? Ensure Comfort, Support & Boot Longevity
- Why are instrumented treadmills essential for validating plantar pressure sensors? Secure Gold Standard Accuracy
- Why use online digital research tools for footwear consumer data? Master Data-Driven Market Strategies
- How does a multi-camera motion capture system validate gait and posture? The Science of Foot Strike Correlations
- What are the key chemical components in footwear waterproofing sprays? Understanding Resins, Solvents, and Propellants
- Why is zinc oxide (ZnO) used with azodicarbonamide (AZD) in EVA foaming? Master Optimal Foam & Protect Materials
- How do high-performance ARM Cortex microcontrollers contribute to sensor signal processing in wearable footwear?
- What is the purpose of using 3D-printed load concentrators in smart insoles? Enhance Sensor Accuracy & Data Fidelity



















