Safety shoes protect you by integrating specialized materials and structural reinforcements designed to shield your feet from a wide range of specific workplace hazards. These features go far beyond simple durability, providing targeted defense against everything from heavy impacts and sharp objects to invisible threats like chemical spills and electrical currents.
The true value of safety footwear isn't found in a single feature, but in its role as a specialized system. Understanding how these distinct protective layers work together is the key to selecting the right shoe that actively mitigates the specific risks of your environment.
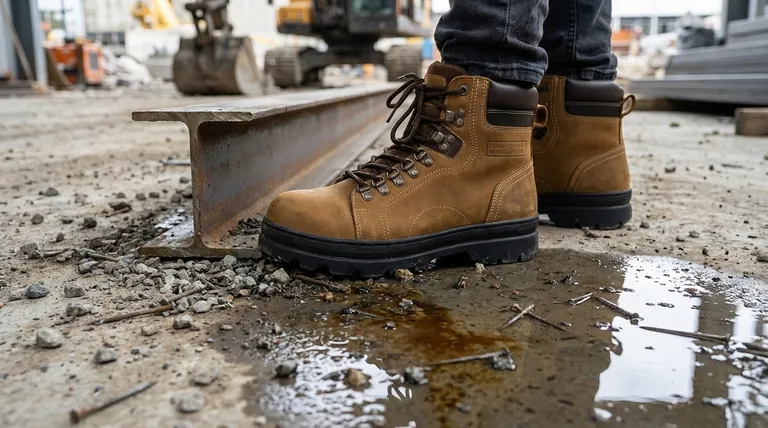

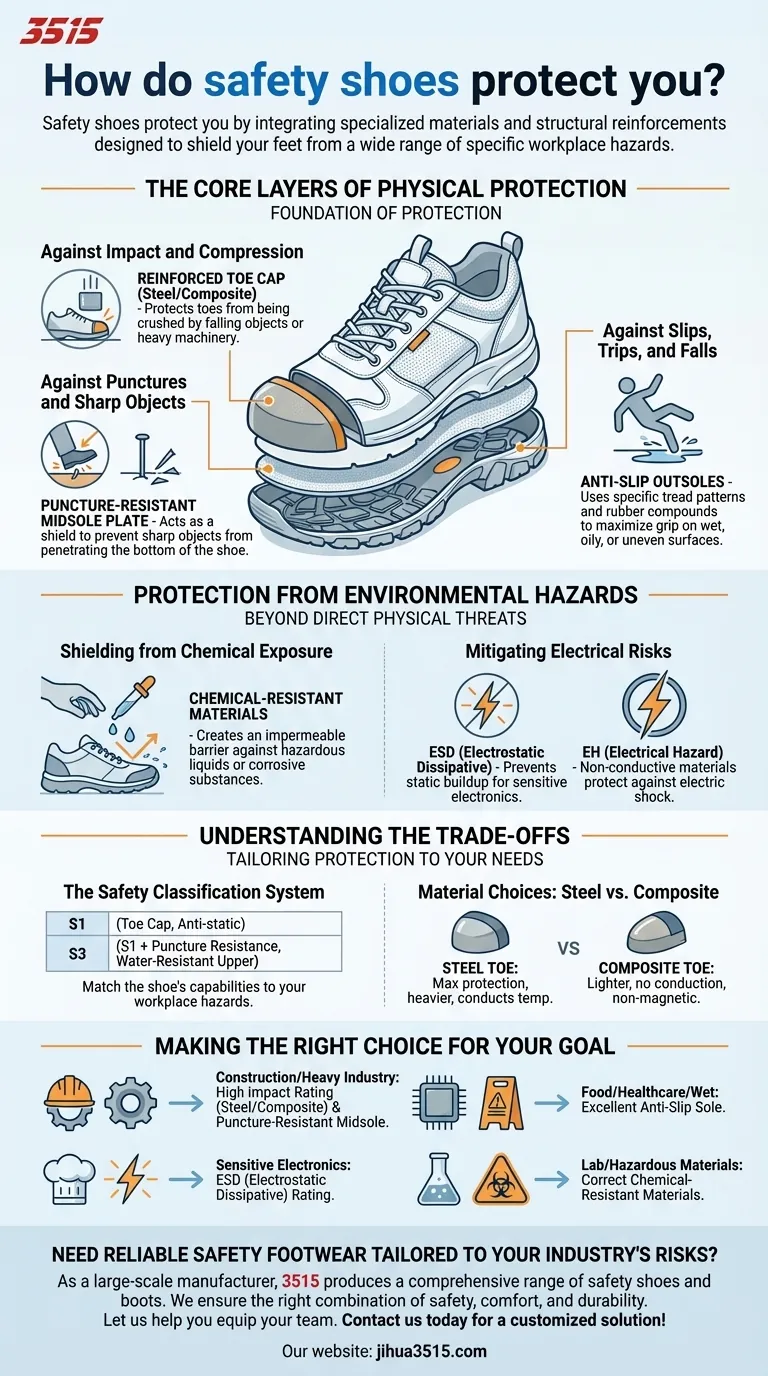
The Core Layers of Physical Protection
The most common understanding of safety footwear revolves around its ability to prevent direct physical injury. These features form the foundation of most protective shoes.
Against Impact and Compression
The most iconic feature of a safety shoe is its reinforced toe cap. This component is engineered to protect your toes from being crushed by falling objects or compressed by heavy machinery.
These caps are typically made from steel or lighter-weight composite materials, both of which are tested to meet specific safety standards for impact resistance.
Against Punctures and Sharp Objects
Many job sites have risks like stray nails, screws, or metal shards on the ground. To counter this, safety shoes often include a puncture-resistant midsole plate.
This plate is positioned between the insole and outsole, acting as a shield to prevent sharp objects from penetrating the bottom of the shoe and injuring your foot.
Against Slips, Trips, and Falls
Slips and falls are among the most frequent causes of workplace injuries. Safety shoes address this with specially designed anti-slip outsoles.
These soles use specific tread patterns and rubber compounds to maximize grip on wet, oily, or uneven surfaces, significantly improving your stability and preventing dangerous falls.
Protection from Environmental Hazards
Beyond direct physical threats, many work environments contain hazards that are less obvious but equally dangerous. Specialized safety footwear is designed to shield you from these risks.
Shielding from Chemical Exposure
For those working with hazardous liquids or corrosive substances, safety shoes are built with chemical-resistant materials like specialized rubber or neoprene.
This creates an impermeable barrier that prevents chemicals from seeping through and causing burns or other serious health complications.
Mitigating Electrical Risks
Safety footwear provides critical protection against electrical hazards. This is typically achieved in two distinct ways.
Electrostatic Dissipative (ESD) footwear is designed to prevent the buildup of static electricity, protecting sensitive electronic components from damage. In contrast, Electrical Hazard (EH) rated shoes are made with non-conductive materials to protect the wearer from electric shock from live circuits.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing safety footwear is not a one-size-fits-all process. The level and type of protection you need are dictated by your specific job, and every feature comes with considerations.
The Safety Classification System
Safety shoes are rated using a standardized classification system (e.g., S1, S1P, S3) that indicates which specific protective features are included.
A basic S1 shoe might have a toe cap and anti-static properties, while a more advanced S3 shoe will also include puncture resistance and a water-resistant upper. This system ensures you can match the shoe's capabilities to your workplace hazards.
Material Choices: Steel vs. Composite
The choice between a steel toe and a composite toe involves trade-offs. Steel toes offer maximum protection but are heavier and conduct temperature.
Composite toes are lighter, do not conduct heat or electricity, and can be more comfortable, making them ideal for environments where metal detectors are present.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The most effective safety shoe is the one that directly addresses the primary risks of your daily work. Use your environment as your guide to determine your priorities.
- If your primary focus is construction or heavy industry: Prioritize a high impact rating (steel or composite toe) and a puncture-resistant midsole.
- If your primary focus is working with sensitive electronics: You must select footwear with a specific ESD (Electrostatic Dissipative) rating.
- If your primary focus is food service, healthcare, or wet environments: An excellent anti-slip sole is your most critical feature for preventing falls.
- If your primary focus is lab work or handling hazardous materials: Ensure the shoe is made from the correct chemical-resistant materials to prevent exposure.
Ultimately, safety footwear is a critical piece of personal protective equipment engineered to prevent injury, and selecting the right features for your role is a crucial step in ensuring your personal safety.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Type | Protective Feature | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Impact & Compression | Reinforced Toe Cap (Steel/Composite) | Protects toes from heavy falling objects |
| Punctures | Puncture-Resistant Midsole Plate | Prevents sharp objects from penetrating the sole |
| Slips & Falls | Anti-Slip Outsole | Improves grip on wet or oily surfaces |
| Chemical Exposure | Chemical-Resistant Materials | Shields feet from hazardous liquids |
| Electrical Risks | ESD/EH Rated Construction | Prevents static buildup or electric shock |
Need reliable safety footwear tailored to your industry's risks?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety shoes and boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities cover all types of protective footwear, ensuring you get the right combination of safety features, comfort, and durability.
Let us help you equip your team with footwear that meets the highest safety standards. Contact us today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- Why is manufacturer diversity and inclusion important in work boot design? For Superior Fit, Safety & Comfort
- Is safety-toe as good as steel toe? Choose the Right Protection for Your Job
- Is safety toe better than steel toe? A Guide to Choosing the Right Protection
- Why is the last important in work boot design? It's the Anatomical Blueprint for Comfort & Safety
- What is a safety-toe in a boot? Your Guide to Choosing the Right Protection



















